The Salesforce Certified Administrator Exam 2024 is a prestigious certification that validates your knowledge and skills in Salesforce. Here are the key details:
- Content: The exam consists of 60 multiple-choice/multiple-select questions and 5 non-scored questions
- Time: You have 105 minutes to complete the exam.
- Passing Score: A score of 65% is required to pass (43 Right Answers)
- Registration Fee: The exam registration fee is USD 200, plus applicable taxes as required per local law.
- Retake Fee: For every retake, the fee is USD 100, plus applicable taxes as required per local law.
Exam Outline
The Salesforce Certified Administrator Exam is designed to test your knowledge and skills in managing Salesforce applications, users, and data, as well as maintaining and customizing Sales Cloud and Service Cloud applications. It covers the breadth of the Salesforce features available for the end-users and configurations for the administrator to assist organizations in getting the best from the platform across the Sales, Service, and Collaboration Clouds
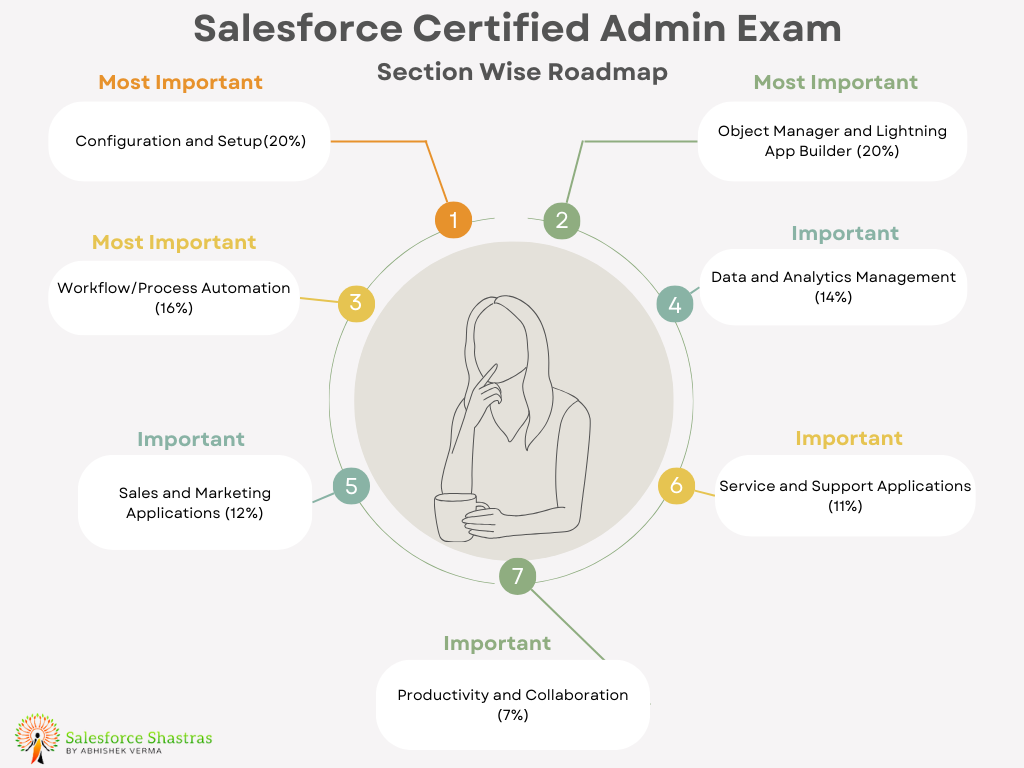
Configuration and Setup (20%): This section will consist of 13 questions from exam and this section tests your knowledge on how to configure and set up Salesforce to meet the specific needs of your organization. It includes understanding of user setup, security settings, and company profile settings.
- User Setup: This involves creating and managing users in Salesforce. You need to understand how to create users, assign them to profiles and permission sets, and manage their access. For example, you might need to create a new user for a new employee, assign them to the “Sales Team” profile, and give them access to the “Opportunities” object.
- Security Settings: This involves setting up the security model in Salesforce to control who can see and do what. This includes setting up organization-wide defaults, role hierarchies, sharing rules, and field-level security. For example, you might need to set up a sharing rule that allows the “Sales Team” to view and edit Opportunities owned by the “Marketing Team”.
- Company Profile Settings: This involves configuring settings that apply to your entire organization. This includes setting your organization’s default language and locale, currency, fiscal year, business hours, and more. For example, you might need to set your organization’s default currency to USD if your company operates primarily in the United States.
- User Interface (UI) Features: This section covers the declarative configuration of the Salesforce UI. It includes understanding UI settings, the app menu, list views, global actions, and the Lightning App Builder. For example, an admin might need to customize the app menu to include specific apps for different user profiles, or configure list views to display relevant data for users.
- Company information: This section involves understanding the options found in the company settings. It includes details like fiscal year, business hours, currency management, and default settings. For instance, the fiscal year setting is crucial for companies that have a non-calendar fiscal year, as it affects forecasting and reporting.
- Locale settings: Locale settings in Salesforce are used to specify the locale of the organization. It affects the format of date, time, and number fields. For example, a company based in the US would have different locale settings compared to a company based in France.
- Search results: This section tests your knowledge on how search is configured and used in Salesforce. It includes understanding how objects and fields are indexed for search, how search results are returned, and how to use advanced search features.
- List views: List views in Salesforce allow users to see a specific set of records in a list. This section tests your ability to create and manage list views. For example, a sales rep might have a list view for “My Opportunities” that only shows opportunity records owned by them.
- Currency management: If your organization sells in more than one currency, you’ll need to understand currency management. This includes setting up the corporate currency, adding additional active currencies, and managing conversion rates.
- Fiscal year: The fiscal year setting in Salesforce is used to define the start and end of a company’s fiscal year. It’s important for accurate forecasting and reporting. For example, if a company’s fiscal year runs from April to March, the admin would need to set this up in Salesforce.
- Default settings: Default settings in Salesforce can include a wide range of configurations, from default field values to default sharing settings. Understanding these settings is crucial for ensuring users have the correct access and data.
- Homepage layouts: Homepage layouts control what components users see on their Salesforce homepage. This could include things like dashboards, tasks, or recent records. For example, a service agent might have a component for “Cases Assigned to Me” on their homepage.
- User management: User management involves creating and managing user records in Salesforce. This includes assigning profiles and permission sets, resetting passwords, and deactivating users. For example, when a new sales rep is hired, the admin would need to create a new user record for them with the correct access.
- Security settings: Salesforce provides various security settings to protect the organization’s data. This includes setting up organization-wide defaults, role hierarchies, sharing rules, and field-level security. For example, you might need to set up a sharing rule that allows the “Sales Team” to view and edit Opportunities owned by the “Marketing Team”. You also need to understand how to configure user authentication and single sign-on, manage user sessions, and set password policies. For instance, you might need to enforce a policy where users are logged out after 15 minutes of inactivity, or where passwords must be at least 10 characters long and include a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Sharing settings: Salesforce provides sharing settings that control the visibility and access of records. This includes understanding the difference between role hierarchies, public groups, sharing rules, manual sharing, team sharing, and Salesforce to Salesforce sharing. For example, you might need to create a sharing rule that gives the “Marketing Team” read/write access to all Opportunity records owned by the “Sales Team”. Or, you might need to set up a role hierarchy that allows managers to view and edit all records owned by their subordinates.
Sample Questions
Question 1: Which type of Fiscal Year setting would you use if your company had a fiscal year that started on January 1st and each quarter was divided into 13 weeks?
- Answer : Custom Fiscal Year. Since the quarters in this scenario are separated by weeks instead of months, you would need to use a Custom Fiscal Year to meet this requirement.
Question 2: Your company has a Custom Fiscal Year that starts on February 15th with each quarter divided into 13-week segments. Your company is now changing their fiscal year to start on January 1st and follow a normal 3-month quarterly fiscal year. What do you change in your Fiscal Year settings to accommodate this change?
- Answer: You would update your Custom Fiscal Year to show January 1st as the start date and change the quarters to be every 3 months. Once you’ve activated a Custom Fiscal Year, you cannot deactivate it, but you can customize it to function exactly like a Standard Fiscal Year.
Question 3: If your company has a fiscal year that starts on June 1st and runs on a 3-month per quarter year, which Fiscal Year setting would you use?
- Answer: Standard Fiscal Year. You can set a Standard Fiscal Year to start on the 1st of any month, following a 3-month per quarter year.
For more sample question & learning resource check out this:
Salesforce – Configuration & Setup Flashcards | Quizlet
Object Manager and Lightning App Builder (20%): This section will consist of 13 questions from exam, This section focuses on your ability to manage objects and fields in Salesforce. You’ll need to understand how to create custom objects and fields, modify page layouts, and build apps using the Lightning App Builder.
- Object Manager: This is a tool in Salesforce that allows you to manage the objects in your org. You can create custom objects, modify existing standard objects, and manage the fields on those objects. For example, you might create a custom object to track Projects, with custom fields for Start Date, End Date, and Project Manager. You can also control the security settings for each object, determining who can see and edit records of that object type.
- Fields: Fields are the individual pieces of data that are stored on each record. In Salesforce, you can create custom fields on both standard and custom objects. For example, on your Project object, you might create a custom picklist field for Project Status, with options like “Not Started”, “In Progress”, and “Completed”. You can also modify the properties of standard fields, like changing the picklist values on the Stage field of an Opportunity.
- Page Layouts: Page layouts control how fields and related lists are displayed on the record detail page. As an admin, you can modify page layouts to make certain fields more prominent, group related fields together, and hide fields that aren’t relevant. For example, you might move the Project Status field to the top of the Project page layout, so it’s the first thing users see when they view a Project record.
- Lightning App Builder: This is a tool in Salesforce that allows you to build custom pages for your Salesforce apps. You can add components to the page, like lists, charts, and custom components, and you can control who can see the page based on their profile or role. For example, you might create a custom app page for your sales team that includes a list view of all open Opportunities, a chart of Opportunities by Stage, and a custom component that shows news articles about their top Accounts.
Sample Questions
Question 1: What is the purpose of the Object Manager in Salesforce?
- Answer 1: The Object Manager in Salesforce is a tool that allows administrators to manage objects and their fields. It is used to create custom objects, manage standard objects, create and manage fields, and set field-level security.
Question 2: How would you create a custom object in Salesforce?
- Answer 2: To create a custom object in Salesforce, navigate to the Object Manager, click on the “Create” dropdown, and select “Custom Object”. Fill in the necessary details such as the label, plural label, and object name, then configure the optional features as needed. Click “Save” to create the custom object.
Question 3: What is the Lightning App Builder and what is its function?
- Answer 3: The Lightning App Builder is a visual tool for creating and customizing Salesforce apps. It allows administrators to build apps by dragging and dropping components onto a canvas, making it easy to design responsive layouts for both desktop and mobile.
Question 4: How can you modify a page layout in Salesforce?
- Answer 4: To modify a page layout, go to the Object Manager and select the object for which you want to change the layout. Click on “Page Layouts”, then select the layout you want to edit. In the layout editor, you can add, remove, or rearrange fields, buttons, and related lists. You can also set field properties and visibility settings. Click “Save” when you’re done making changes.
Question 5: How do you build an app using the Lightning App Builder?
- Answer 5: To build an app using the Lightning App Builder, click on “App Manager” in the Setup menu, then click “New Lightning App”. Fill in the app details, then click “Next”. In the App Builder interface, you can add, arrange, and configure components to build your app. Once you’re satisfied with your app, click “Save” and then “Activate” to make the app available to users.
Sales and Marketing Applications (12%): This section will consist of 7-8 questions from exam, This section assesses your understanding of the Sales and Marketing applications available in Salesforce. You’ll need to know how to manage leads, opportunities, products, price books, and campaigns.
- Leads: Leads in Salesforce represent potential business opportunities. You need to understand how to create, manage, and convert leads. For example, a lead might be created when someone fills out a form on your company’s website. You would then manage that lead, tracking your communications with them and any other relevant information. When the lead is ready to make a purchase, you would convert the lead into an account, contact, and opportunity.
- Opportunities: Opportunities represent potential sales and are linked to accounts and contacts. You need to understand how to create and manage opportunities, including tracking the stage of the sale, the potential revenue, and the expected close date. For example, after converting a lead, you might create an opportunity to track a potential sale.
- Products and Price Books: Products represent the items or services your company sells, and they can be linked to opportunities to track potential revenue. Price Books are used to set the standard and custom prices for your products. For example, you might have a product that represents a service your company provides, and you could use a Price Book to set the standard price for that service.
- Campaigns: Campaigns in Salesforce track marketing efforts. You need to understand how to create and manage campaigns, including tracking the status, start and end dates, expected revenue, and actual revenue. For example, you might create a campaign to track a marketing email blast, and you would use the campaign to track how many leads were generated and how much revenue was ultimately produced from those leads.
Sample Questions
Question 1: Ursa Major Solar has created a new product line of solar panels with a special sales team to sell these products. The sales process for the new line is more complex than the current sales process and requires additional stages to the sales path. How should the system administrator configure Salesforce to ensure only the appropriate stages are visible based on the product line?
- Answer 1: The system administrator should create a new sales process to determine which stages appear for this new product line. Additionally, a new Opportunity record type should be created to display a unique page layout for this new product line.
Question 2: A marketing team has launched a new campaign for a product. They want to track the number of leads generated from this campaign and the revenue generated from these leads. How can this be achieved in Salesforce?
- Answer 2: The marketing team can create a new Campaign in Salesforce and associate all the leads generated from this campaign to it. As these leads are converted into opportunities and eventually result in sales, the revenue can be tracked at the campaign level.
Question 3: Your company sells multiple products, each with different pricing. They want to offer special pricing for a specific set of customers. How can this be implemented in Salesforce?
- Answer 3: In Salesforce, this can be achieved by using Price Books. A new Price Book can be created for the specific set of customers with the special pricing for the products. When an opportunity is created for these customers, the special Price Book can be used.
Service and Support Applications (11%): This section will consist of 6-8 questions from exam In this section, you’ll be tested on your knowledge of the Service Cloud and support applications. This includes understanding case management, solutions, knowledge, entitlements, and Service Cloud console.
- Case Management: This involves managing customer issues or inquiries, known as cases in Salesforce. You need to understand how to create, assign, escalate, and resolve cases. For example, a customer might submit a case because they’re having trouble using a feature of your product. You would then assign that case to a support agent, who would work on resolving the issue.
- Solutions: Solutions in Salesforce are detailed descriptions of customer issues and the methods used to resolve them. They provide a way to share knowledge among support agents and customers. For example, if multiple customers have the same issue, you can create a solution that details how to resolve that issue. Then, when a support agent encounters the issue, they can find the solution and resolve the case more quickly.
- Knowledge: Salesforce Knowledge is a knowledge base where you can create, store, manage, and share information. For example, you can create knowledge articles that provide information about your products and services. These articles can be used internally by your support agents, or externally by your customers.
- Entitlements: Entitlements in Salesforce are used to determine the kind of support a customer is entitled to receive. For example, one customer might be entitled to phone support, while another customer is only entitled to email support.
- Service Cloud Console: The Service Cloud Console is a user interface that provides support agents with a unified view of all the relevant information needed to assist customers. For example, in the console, an agent can view a customer’s open cases, contact information, and activity history all in one place.
Sample Questions
Question 1: Your company uses Salesforce Service Cloud for case management. A customer has reported an issue via email. How can this email be converted into a case in Salesforce?
Answer 1: Salesforce provides Email-to-Case functionality which allows you to automatically convert customer emails into cases. The system captures the entire email, including attachments, as a case in Salesforce, allowing your support team to track and respond to the case.
Question 2: You are a Salesforce admin for a company that uses Salesforce Knowledge. The support team often encounters similar cases. How can Salesforce Knowledge be used to improve the efficiency of resolving these cases?
- Answer 2: Salesforce Knowledge allows you to create and manage a knowledge base with articles that provide solutions to common issues. When similar cases are encountered, support agents can quickly search the knowledge base for relevant articles and attach them to the case, improving efficiency and consistency in resolving cases.
Question 3: Your company provides different levels of support to customers based on their contract. How can you ensure that a customer receives the appropriate level of support in Salesforce?
- Answer 3: In Salesforce, you can use Entitlements to define the support terms for each customer. Entitlements specify what kind of support a customer is entitled to, including the support hours, response times, and the duration of the support. This ensures that each customer receives the appropriate level of support based on their contract.
Question 4: What is the purpose of the Service Cloud Console and how does it benefit service agents?
- Answer 4: The Service Cloud Console is a user interface designed for service agents. It provides a unified view of all relevant customer data, including cases, contacts, accounts, and knowledge articles, in one screen. This allows service agents to work on multiple records at once and quickly find the information they need, improving their productivity and the quality of customer service.
Productivity and Collaboration (7%): This section will consist of 5-6 questions from exam, This section tests your knowledge on Salesforce’s productivity and collaboration features. This includes understanding of Chatter, Salesforce Mobile, and activity management.
- Chatter: Chatter is Salesforce’s collaboration tool that connects every employee with the files, data, and experts they need. It allows users to collaborate on sales opportunities, service cases, campaigns, and projects with embedded apps and custom actions. For example, a sales rep might post a question about a difficult sales opportunity, and anyone in the company can respond with their advice or insights.
- Salesforce Mobile: This is Salesforce on the go. The Salesforce mobile app puts all your vital information at your fingertips, including dashboards, reports, tasks, and more. You need to understand how to configure the mobile app and manage its settings. For example, you might need to create compact layouts and action layouts for the mobile app, or enable offline access for your mobile users.
- Activity Management: This involves managing tasks, events, public calendars, and multi-day events. For example, a sales rep might use tasks to track their to-do items, like following up with a lead or preparing a quote. They might use events to schedule their meetings and calls. As an admin, you need to understand how to configure activity settings, like enabling shared activities or setting up activity reminders.
Sample Questions
Question 1: A sales representative at your company is often on the road and needs to update Opportunities from their mobile device. How can Salesforce Mobile help in this scenario?
- Answer 1: Salesforce Mobile allows users to access Salesforce from their mobile devices. The sales representative can use the Salesforce Mobile app to view, edit, and update Opportunities while on the road, ensuring they have real-time access to their data.
Question 2: Your team uses Chatter to collaborate on sales deals. A new team member has joined and needs to get up to speed quickly. How can Chatter be used to assist the new team member?
- Answer 2: The new team member can follow relevant people, groups, and records in Chatter. This will allow them to see updates and conversations about the sales deals in their Chatter feed. They can also ask questions and participate in conversations to gain more context and knowledge.
Question 3: A manager wants to ensure that tasks related to customer follow-ups are not missed. How can activity management in Salesforce assist with this?
- Answer 3: Activity management in Salesforce allows users to create, track, and manage tasks and events. The manager can create tasks for customer follow-ups and assign them to the appropriate team members. These tasks will appear on the team members’ activity timelines, ensuring they are aware of the tasks and their due dates.
Data and Analytics Management (14%): This section will consist of 9-10 questions from exam, This section covers your understanding of how to manage data in Salesforce. It includes topics like data import and export, reports and dashboards, and data quality.
- Data Import and Export: This involves understanding how to use tools like the Data Import Wizard and Data Loader to import data (like accounts, contacts, leads, and custom objects) into Salesforce, and how to export data from Salesforce. For example, you might use the Data Import Wizard to import a CSV file of leads that you got from a marketing event, or use the Data Loader to export all your account data for backup purposes.
- Reports and Dashboards: This involves creating, customizing, and managing reports and dashboards in Salesforce. Reports provide a way to create custom views of your data, while dashboards provide a visual representation of your data. For example, you might create a report that shows all opportunities that are set to close this month, and then use a dashboard to display a chart of those opportunities by stage.
- Data Quality: This involves understanding how to maintain the quality of your data in Salesforce. This includes managing duplicate records, validating data on input, and keeping your data clean and up-to-date. For example, you might use duplicate rules to prevent users from creating duplicate contacts, or use validation rules to ensure that important fields are filled out when a user creates a new opportunity.
Sample Questions
Question 1: Your company has a large amount of data that needs to be imported into Salesforce. What tool can you use to accomplish this and why?
- Answer 1: For large amounts of data, the Data Loader tool can be used. It is a client application that supports bulk import or export of data, as well as the deletion and insertion of data. It can process large amounts of data that the Data Import Wizard might not be able to handle.
Question 2: A sales manager wants to track the performance of each sales representative in terms of the number of deals closed every month. How can this be achieved in Salesforce?
- Answer 2: This can be achieved by creating a report in Salesforce. The report can be set up to group data by sales representative and by month, and to count the number of deals closed. This report can then be displayed on a dashboard for easy access and visualization.
Question 3: There are concerns about the quality of data in Salesforce due to duplicate records. How can this issue be addressed?
- Answer 3: Salesforce provides several tools to maintain data quality, including duplicate management tools. Duplicate Rules can be set up to identify potential duplicates when records are created or edited. Matching Rules can be defined to determine how records are compared for duplicates.
Workflow/Process Automation (16%): This section will consist of 10-11 questions from exam, This section assesses your ability to automate standard and repetitive tasks in Salesforce. You’ll need to understand how to use workflow rules, process builder, and approval processes.
- Workflow Rules: Workflow rules in Salesforce are one of the ways to automate standard and repetitive business processes. They let you automate standard internal procedures and processes to save time across your org. A workflow rule is the main container for a set of workflow instructions. For example, you might have a workflow rule that sends an email to the sales team whenever a new high-value opportunity is created.
- Process Builder: Process Builder is a visual tool that allows you to build complex processes by configuring either immediate or time-based actions to be taken when a record changes in some way. You can use it to perform more than one action and to launch a flow. You can also use it to create a record, update related records, or even send an email. For example, you could use Process Builder to create a new task for a user whenever a high-value opportunity is closed.
- Approval Processes: Approval processes are used to approve records in Salesforce. They specify the steps necessary for a record to be approved and who must approve it at each step. This is useful for situations where a record, such as a discount or a contract, needs to be approved by one or more people. For example, you might create an approval process for discounts that automatically sends an approval request to a manager when a sales rep creates a discount over a certain amount.
Sample Questions
Question 1: A company wants to automate the process of updating the status of an opportunity to ‘Negotiation/Review’ when a quote related to that opportunity is approved. Which automation tool should be used in Salesforce to achieve this?
- Answer 1: This can be achieved using Process Builder. A process can be created that starts when a record changes, specifically when a Quote record is updated. The process can then have a criteria node that checks if the Quote’s status is ‘Approved’. If the criteria is met, an immediate action can be set to update the related Opportunity’s stage to ‘Negotiation/Review’.
Question 2: Your organization wants to automate the process of sending an email to the account owner whenever a high-value opportunity is closed. How can this be achieved in Salesforce?
- Answer 2: This can be achieved using Workflow Rules. A workflow rule can be created on the Opportunity object with criteria that checks if the Opportunity is closed and if its value is above the high-value threshold. If the criteria is met, an email alert can be set as the workflow action to send an email to the Account Owner.
Question 3: A company has a multi-step approval process for discounts on opportunities. The process involves approval from a sales manager and then a finance manager. How can this be set up in Salesforce?
- Answer 3: This can be set up using Approval Processes in Salesforce. An approval process can be created on the Opportunity object with initial submission criteria that checks if a discount has been applied. The process can then have two approval steps, one for the sales manager and one for the finance manager. Each step can be set to assign the approval request to the respective manager.
Resources:
Salesforce quizlet by bradley_benton8
Salesforce Administrator Practice Exam with 30 Questions and Answers
Note: Remember, these are just sample questions and the actual exam may contain different types of questions. It’s important to thoroughly understand the concepts and functionalities of Salesforce for the exam


